Kidney Stones vs UTI: How to Determine and Deal With Each Problem Effectively
Kidney Stones vs UTI: How to Determine and Deal With Each Problem Effectively
Blog Article
A Comprehensive Evaluation of Therapy Options for Kidney Stones Versus Urinary Tract Infections: What You Need to Know
The distinction in between therapy alternatives for kidney stones and urinary system infections (UTIs) is crucial for efficient client management. While UTIs are usually addressed with antibiotics that offer rapid relief, the technique to kidney stones can vary considerably based on specific factors such as stone dimension and structure. Non-invasive techniques like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) might be appropriate for smaller stones, yet larger or obstructive stones commonly call for even more intrusive techniques. Understanding these subtleties not just educates professional decisions yet likewise boosts person results, inviting a more detailed assessment of each condition's therapy landscape.
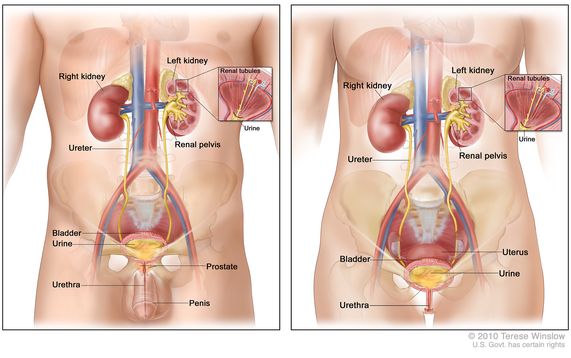
Understanding Kidney stones
Kidney stones are tough deposits formed in the kidneys from salts and minerals, and understanding their make-up and development is essential for reliable monitoring. The main sorts of kidney stones include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, struvite, uric acid, and cystine stones, each with distinctive biochemical origins. Calcium oxalate stones are one of the most common, commonly resulting from high levels of calcium and oxalate in the urine. Variables such as dehydration, nutritional habits, and metabolic disorders can add to their development.
The development of kidney stones occurs when the concentration of particular materials in the urine enhances, causing formation. This crystallization can be influenced by urinary system pH, volume, and the presence of inhibitors or promoters of stone formation. Low urine volume and high acidity are conducive to uric acid stone advancement.
Comprehending these variables is important for both prevention and treatment (Kidney Stones vs UTI). Effective management strategies may include dietary modifications, enhanced fluid intake, and, sometimes, medicinal interventions. By acknowledging the underlying reasons and sorts of kidney stones, doctor can execute tailored approaches to mitigate recurrence and improve patient outcomes
Review of Urinary System Tract Infections
Urinary system system infections (UTIs) are typical microbial infections that can influence any type of part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most of UTIs are triggered by Escherichia coli (E. coli), a kind of bacteria normally found in the intestines. Females are a lot more prone to UTIs than guys because of anatomical distinctions, with a much shorter urethra helping with less complicated bacterial access to the bladder.
Symptoms of UTIs can differ depending on the infection's area yet commonly include constant peeing, a burning sensation throughout urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pelvic discomfort. In more extreme situations, especially when the kidneys are entailed, symptoms might also include high temperature, chills, and flank discomfort.
Risk aspects for creating UTIs include sexual activity, specific kinds of birth control, urinary system system problems, and a weakened immune system. Prompt treatment is necessary to prevent problems, including kidney damage, and normally entails prescription antibiotics customized to the specific bacteria involved.
Treatment Choices for Kidney stones

If the stones are bigger or trigger considerable pain, non-invasive procedures such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) may be employed. This technique makes use of audio waves to damage the stones right into smaller fragments that can be more easily travelled through the urinary system system.
In situations where stones are as well big for ESWL or if they obstruct the urinary system, ureteroscopy might be suggested. This minimally invasive treatment entails using a tiny range to break or remove up the stones directly.
Therapy Choices for UTIs
How can medical care companies efficiently address urinary system system infections (UTIs)? The main strategy involves an extensive evaluation of the patient's signs and symptoms and case history, adhered to by proper diagnostic screening, such as urinalysis and pee culture. These examinations assist identify the original microorganisms and determine their antibiotic sensitivity, directing targeted treatment.
First-line treatment typically consists of prescription antibiotics, with options such as nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, relying on local resistance patterns. For straightforward cases, a brief course of anti-biotics (3-7 days) is commonly adequate. In recurrent UTIs, carriers may take into consideration alternative methods or prophylactic anti-biotics, including visite site way of living my company modifications to minimize threat elements.
For individuals with complicated UTIs or those with underlying health and wellness concerns, a lot more hostile treatment might be necessary, potentially entailing intravenous antibiotics and further diagnostic imaging to analyze for issues. Additionally, client education and learning on hydration, health practices, and symptom administration plays a critical role in prevention and reappearance.
Comparing Outcomes and Efficiency
Examining the results and efficiency of treatment choices for urinary system infections (UTIs) is crucial for enhancing individual care. The main treatment for uncomplicated UTIs generally involves antibiotic therapy, with alternatives such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, fosfomycin, and nitrofurantoin. Research studies suggest high effectiveness rates, with the majority of individuals experiencing sign relief within 48 to 72 hours. Nonetheless, antibiotic resistance is an expanding worry, requiring careful choice of prescription antibiotics based on local resistance patterns.
In comparison, therapy results for kidney stones vary substantially based site web on stone location, dimension, and make-up. Choices range from conservative management, such as hydration and pain control, to interventional treatments like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and ureteroscopy. While ESWL has a high success rate for smaller sized stones, issues can emerge, necessitating additional treatments.
Inevitably, the effectiveness of treatments for both problems pivots on precise medical diagnosis and tailored methods. While UTIs normally react well to antibiotics, kidney stone management may need a diverse approach. Constant evaluation of therapy end results is crucial to enhance client experiences and minimize reappearance prices for both UTIs and kidney stones.
Verdict
In recap, treatment methods for kidney stones and urinary system tract infections differ dramatically due to the distinctive nature of each problem. Non-invasive methods such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy are appropriate for smaller stones, whereas larger or obstructive stones might need ureteroscopy.
While UTIs are usually addressed with anti-biotics that give fast relief, the approach to kidney stones can differ substantially based on private factors such as stone size and make-up. Non-invasive techniques like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) may be appropriate for smaller stones, yet bigger or obstructive stones commonly need even more invasive techniques. The key types of kidney stones include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, struvite, uric acid, and cystine stones, each with distinct biochemical beginnings.In contrast, therapy outcomes for kidney stones vary substantially based on stone place, dimension, and make-up. Non-invasive techniques such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy are suitable for smaller stones, whereas larger or obstructive stones might require ureteroscopy.
Report this page